Titanium alloys are at the forefront of advanced material science, revered for their exceptional properties across numerous high-performance sectors. Among the commercially pure and alloyed titanium grades, Gr2 and Gr5 stand as two of the most frequently specified options. Understanding the distinct characteristics and applications of these two grades is paramount for engineers and procurement specialists seeking optimal material selection. This exposition delineates the fundamental differences between Gr2 titanium and Gr5 titanium, providing clarity for precise application matching.
Decoding Commercially Pure Gr2 Titanium
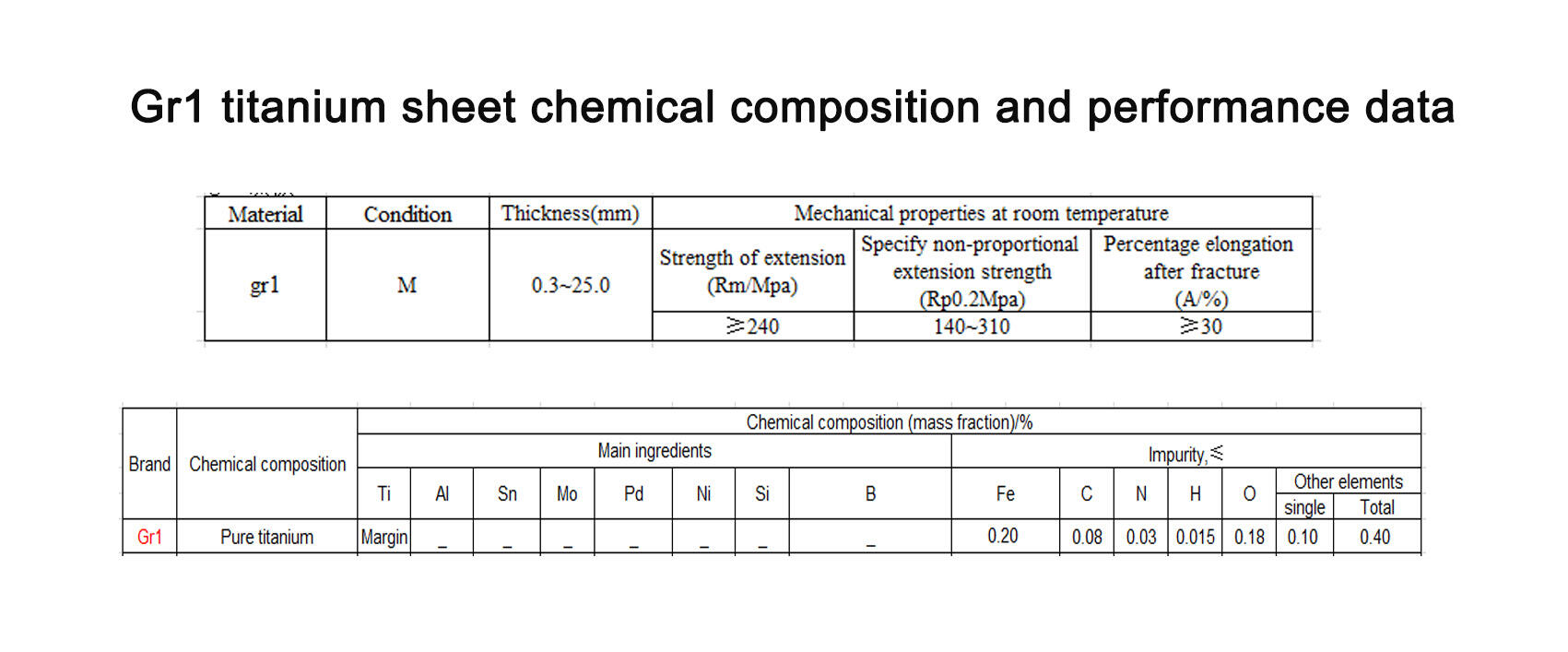
Gr2 titanium, often designated as CP Grade 2, represents one of the most widely utilized commercially pure titanium grades. Its composition is characterized by a minimum of 99.2% titanium, with controlled amounts of oxygen, iron, hydrogen, nitrogen, and carbon. This unalloyed nature grants Gr2 a specific set of attributes that are highly advantageous in various industrial contexts.
The primary distinction of Gr2 lies in its superior corrosion resistance, particularly in oxidizing and mildly reducing environments. It exhibits excellent resistance to seawater, chloride solutions, and a broad spectrum of acids and alkalis, making it an ideal choice for marine, chemical processing, and desalination equipment. Furthermore, Gr2 titanium boasts excellent ductility and formability. Its relatively low tensile strength and high elongation allow for easy cold forming, bending, and welding, facilitating complex fabrications without compromising material integrity. This ease of processing contributes to cost-effective manufacturing for components requiring intricate shapes or extensive forming. Its robust weldability ensures strong and reliable joints, a critical factor for large-scale constructions and assemblies.
Typical applications for Gr2 titanium include heat exchangers, condenser tubing, chemical processing equipment, exhaust components, and marine architectural elements. Its biocompatibility also renders it suitable for certain non-implantable medical devices and components where high strength is not the primary requirement.
Unpacking the Strength of Gr5 Titanium
In stark contrast to its commercially pure counterpart, Gr5 titanium (Ti-6Al-4V) is an alpha-beta alloy, meaning it incorporates alloying elements to significantly enhance its mechanical properties. The addition of 6% aluminum and 4% vanadium is the cornerstone of its superior strength, making it the most commonly specified titanium alloy globally.
The defining characteristic of Gr5 titanium is its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio. This attribute is critical for aerospace, defense, and high-performance automotive sectors, where weight reduction directly translates to improved fuel efficiency and enhanced operational capabilities. Gr5 exhibits significantly higher tensile and yield strengths compared to Gr2, providing robust structural integrity under demanding loads. Despite its superior strength, Gr5 maintains commendable fracture toughness and resistance to fatigue crack propagation. It also offers good resistance to many corrosive environments, though generally not as universal as Gr2 in highly oxidizing acids. Its elevated temperature performance is notably better than pure titanium grades, allowing for applications in more thermally stressed environments.
Fabrication of Gr5 titanium requires more specialized techniques due to its higher strength and reduced ductility compared to Gr2. While it can be welded, forming typically requires hot forming methods. Common applications for Gr5 include aircraft structural components, engine parts, fasteners, landing gear, medical implants (such as bone plates and prosthetics), high-performance automotive components, and marine pressure vessels. Its biocompatibility, combined with high strength, makes it the preferred material for many critical medical implant devices.
Key Differentiators Summarized
The fundamental differences between Gr2 and Gr5 titanium pivot on their composition and resulting mechanical properties:
Composition: Gr2 is commercially pure titanium, while Gr5 is an alloy with aluminum and vanadium.
· Strength: Gr5 possesses significantly higher tensile and yield strengths than Gr2.
· Ductility & Formability: Gr2 offers superior ductility and is easier to cold form and weld. Gr5, while strong, requires hot forming for intricate shapes and specialized welding.
· Corrosion Resistance: Gr2 generally offers more universal corrosion resistance, especially in highly oxidizing media. Gr5 provides excellent corrosion resistance suitable for many applications, particularly in marine and aerospace environments.
· Applications: Gr2 is favored for chemical processing, desalination, and general corrosive environments where formability is key. Gr5 is predominant in aerospace, medical implants, and high-performance structural applications demanding ultimate strength and lightweight characteristics.
· Cost: Gr2 typically presents a more cost-effective solution for applications where its specific properties are sufficient, while Gr5's enhanced performance often justifies a higher material cost.
Conclusion
Choosing between Gr2 titanium and Gr5 titanium hinges entirely on the specific requirements of the application. For projects prioritizing extreme corrosion resistance, ease of fabrication, and moderate strength, Gr2 stands as an excellent choice. Conversely, when maximum strength-to-weight ratio, high-temperature performance, and robust structural integrity are paramount, Gr5 is the material of preference. A thorough understanding of environmental conditions, mechanical load requirements, and manufacturing capabilities is essential for making an informed decision.
We provide a comprehensive range of Gr2 and Gr5 titanium products, manufactured to rigorous industry standards. Our commitment to material excellence ensures that you receive precision-engineered titanium solutions tailored to your project's demands.
Connect with Our Material Specialists
For further consultation on selecting the ideal titanium grade for your specific application or to discuss your material requirements, please do not hesitate to reach out. Our experienced team is prepared to provide expert guidance and support for your critical projects.
1. ASTM B265, "Standard Specification for Titanium and Titanium Alloy Strip, Sheet, and Plate."
2. AMS 4911, "Titanium Alloy, Sheet, Strip, and Plate, 6Al - 4V, Annealed."
3. ASM International, ASM Handbook Volume 2: Properties and Selection: Nonferrous Alloys and Special-Purpose Materials.
4. Donachie, Matthew J. Jr., Titanium: A Technical Guide. ASM International, 2000.
5. Lütjering, Gerd, and James C. Williams, Titanium. Springer, 2007.
 Hot News
Hot News