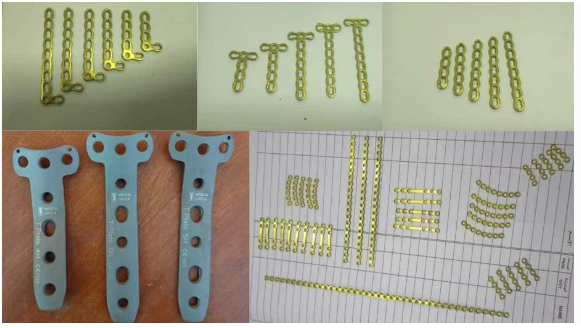
ASTMF 136 GR23 Titanium Sheet is a medical implant mainly used in surgical procedures, especially in orthopedics and maxillofacial surgery. Essentially, it is a plate-like fixation device made of pure titanium or titanium alloys (the most common being Ti-6Al-4V, which contains 6% aluminum and 4% vanadium). During the surgery, the doctor will use specialized screws to fix the titanium plate to both sides of the fractured or cut bone, just like an "internal splint", providing stable support and fixation for the bone, thereby facilitating its proper healing in the correct position. Advantages of Medical Titanium Plates
Excellent biocompatibility
This is the most important advantage of titanium. Titanium is an inert metal. When it comes into contact with human tissues, blood and body fluids, it rarely causes rejection or toxic reactions. Human tissues can tolerate titanium implants very well, significantly reducing the risks of infection and complications.
High strength and low weight ratio (high specific strength)
Titanium has extremely high strength, comparable to that of steel, but its density (weight) is only about half that of steel. This means that titanium plates are strong enough to withstand the daily load of the human body, while not causing a heavy burden to the patient.
Excellent corrosion resistance
The surface of the titanium will naturally form a dense and stable oxide film (titanium dioxide), which can effectively prevent the implant from being corroded and rusted in the complex body fluid environment of the human body, ensuring the long-term stability and safety of the implant.
The "elastic modulus" is similar to that of bones.
The elastic modulus can be regarded as the "stiffness" of a material. The elastic modulus of titanium is much lower than that of traditional metals such as stainless steel, and is closer to the stiffness of human bones. This can effectively reduce the "stress shielding effect" - that is, the hard implant bears most of the stress, causing the underlying bones to become loose and fragile due to the lack of necessary mechanical stimulation. Titanium plates allow more stress to be transferred to the bones, which is beneficial for the healthy healing and remodeling of the bones.
Non-magnetic and good light transmittance
Non-magnetic: Titanium is non-magnetic, which means that patients are safe during MRI examinations and there will be no danger due to the heating or movement of the implant. This is crucial for patients who require MRI follow-up after surgery.
CT/MRI compatibility: Titanium implants may produce some artifacts during CT scans, but they are much smaller compared to stainless steel ones, and do not affect MRI imaging.
Titanium is regarded as a metal that can achieve "osseointegration" with bone tissue, meaning that bone cells can grow directly on the surface of the titanium, forming a strong and direct bond with the implant, rather than being encapsulated by fibrous tissue. This provides an extremely stable and long-term fixation effect.
Specifications:
Property |
Value |
Grade |
ASTM F136 Ti6AL4V ELI |
Composition |
90% Titanium, 6% Aluminum, 4% Vanadium |
Density |
4.43 g/cm³ |
Yield Strength (Annealed) |
895 MPa (130 Ksi) minimum |
Tensile Strength |
930-1,100 MPa (135-160 Ksi) |
Elongation |
10-15% |
Modulus of Elasticity |
113.8 GPa |
Hardness |
30-40 HRC |
Melting Point |
1,670°C (3,038°F) |
Weldability |
Excellent (TIG, MIG, and Laser welding) |
Biocompatibility |
Exceptional (suitable for implants) |
Orthopedics (Trauma and Spine)
Internal fixation for fractures: This method is used for severe fractures of the limbs (such as the humerus, ulna and radius of the arm, femur, tibia and fibula of the leg), intra-articular fractures, and comminuted fractures. The titanium plate can firmly fix the fracture fragments together, creating conditions for healing.
Spinal fusion surgery: This is an intervertebral fusion surgery for the cervical, thoracic, and lumbar vertebrae. It uses a titanium plate system to fix the vertebrae, stabilizing the spine and treating conditions such as intervertebral disc protrusion, spinal slippage, and spinal curvature.
Joint replacement revision surgery: In revision surgeries following the failure of hip or knee joint replacements, titanium plates are often used to repair damaged bone defects.
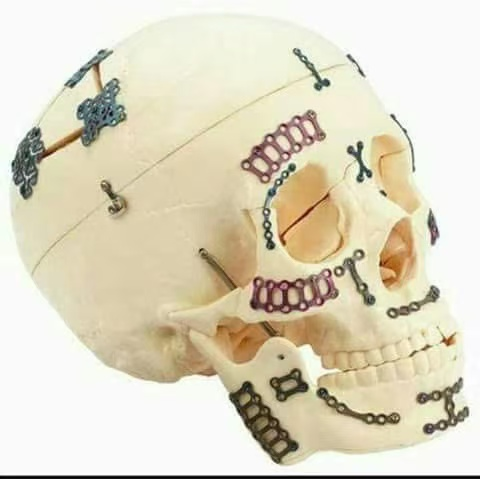
Maxillofacial Surgery and Craniofacial Surgery
Jawbone fracture: Repair fractures of the maxilla and mandible caused by trauma.
Orthognathic surgery: During the correction of jawbone deformities such as mandibular advancement and maxillary retraction, titanium plates are used to fix the separated bone segments.
Skull repair: Used to repair skull defects caused by trauma or surgery.
Zygomatic and orbital bone reconstruction: Repairing complex fractures in the medical face area.
When the alveolar bone condition is poor, very small titanium plates (referred to as "titanium meshes") are used to guide bone regeneration, providing sufficient bone volume for the subsequent implantation of dental implants.
Q: Can I get samples before placing a bulk order?
A: Yes, we offer samples for most products. Please contact us for details.
Q: Can you customize the products?
A: Yes, we offer customization for specifications, packaging, and design. Contact us to discuss your needs.
Q: How do I make a payment?
A: We accept bank transfer (T/T), PayPal, and alibaba.
Q: How do you guarantee the quality of your products?
A: We conduct strict quality control and provide certifications and testing reports for all products.